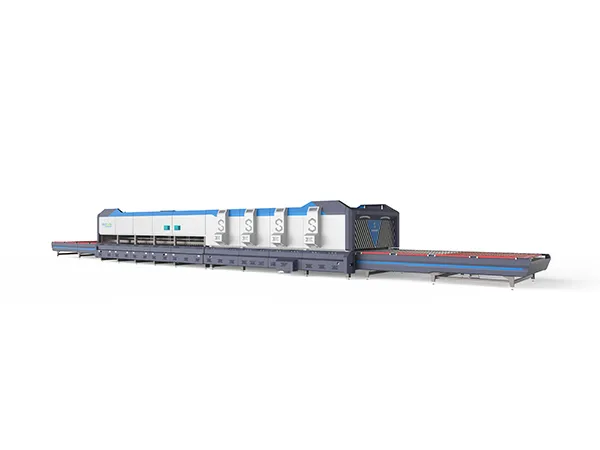
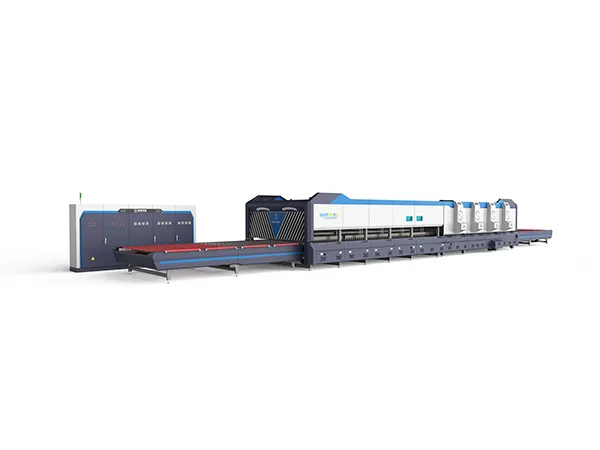
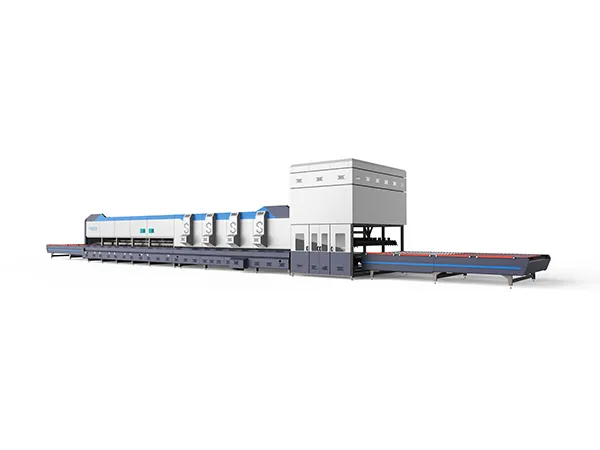
A glass tempering furnace is a specialized piece of equipment used in the production of tempered glass. Tempered glass, also known as toughened glass, is much stronger and safer than regular glass because it undergoes a controlled heating and rapid cooling process that alters its internal structure.The operation of a glass tempering furnace involves several steps to heat, cool, and strengthen glass panels.
Working principle of glass tempering furnace
Loading: Glass panels are loaded onto the entry side of the tempering furnace. Depending on the furnace design, this may be done manually or automatically using a conveyor system.
Preheating: The glass panels enter the preheating zone of the furnace, where they are gradually heated to the desired temperature. This helps to minimize thermal shock and ensure uniform heating throughout the glass.
Heating: Once the glass panels have been preheated, they move into the main heating zone of the furnace. Here, the temperature is raised to the point where the glass becomes soft and pliable. The heating process is carefully controlled to achieve the desired tempering characteristics while avoiding overheating or thermal distortion.
Quenching: After reaching the appropriate temperature, the glass panels move into the quenching zone of the furnace. In this zone, the glass is rapidly cooled using either forced air or high-pressure air jets. This rapid cooling creates a state of high compression on the surface of the glass, while the interior remains in tension, resulting in tempered glass with increased strength and resistance to breakage.
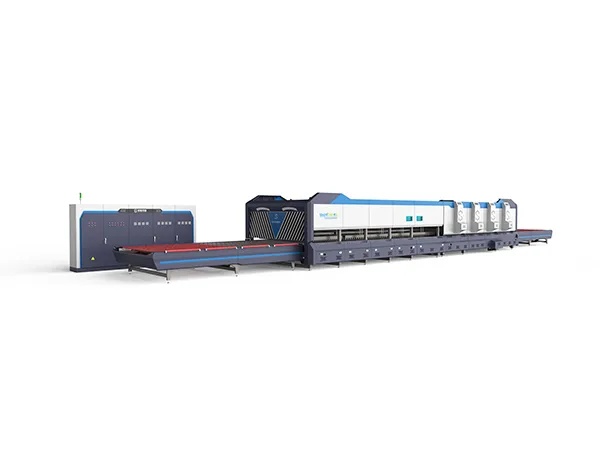

Cooling: After quenching, the tempered glass panels move into the cooling zone of the furnace, where they are gradually cooled to room temperature. This annealing process helps to relieve any remaining internal stresses in the glass and ensure uniformity of the tempered glass.
Unloading: Finally, the tempered glass panels are unloaded from the furnace and either transferred to a storage area or prepared for further processing, such as cutting, edge finishing, or packaging.
Throughout the operation of the tempering furnace, various sensors and control systems monitor key parameters such as temperature, heating rate, and cooling rate to ensure consistent and high-quality tempering results. Additionally, safety features such as interlocks and emergency stop mechanisms are in place to protect personnel and equipment from accidents or malfunctions.
It's important to note that the specific operation of a tempering furnace may vary depending on factors such as the furnace design, the type of glass being tempered, and the production requirements of the facility.
Glass tempering furnace operation
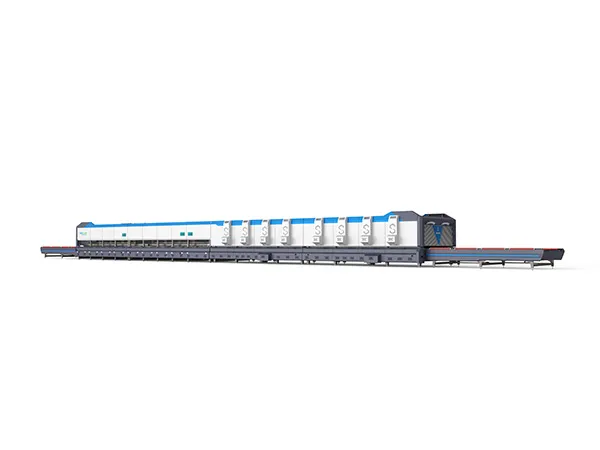

Preparation
-
Inspect the furnace and ensure that it is clean and in proper working condition.
-
Verify that all safety mechanisms are functioning correctly.
-
Check the heating elements, fans (if applicable), and cooling system to ensure they are operational.
Loading
-
Place the glass panels onto the loading conveyor or roller bed of the furnace.
-
Ensure that the panels are properly spaced and positioned to allow for uniform heating and cooling.
Heating
-
Start the heating process by activating the heating elements or burners.
-
Monitor and control the temperature of the furnace to ensure that it reaches the desired heating temperature gradually and uniformly.
-
Depending on the type of furnace, adjust the heating settings and airflow to achieve the desired heating profile for the specific type and thickness of glass being tempered.
Quenching:
-
Once the glass panels reach the required temperature for tempering, initiate the quenching process.
-
If using forced air cooling, activate the blowers to rapidly cool the glass panels.
-
Ensure that the cooling process is uniform across all sections of the glass panels to prevent uneven tempering and potential distortion.
-
Monitor and adjust the cooling airflow and pressure as needed to achieve the desired tempering results.
Annealing:
-
After quenching, the glass panels undergo an annealing process to relieve any remaining internal stresses and ensure stability.
-
Gradually reduce the temperature of the furnace to allow the glass panels to cool slowly and uniformly.
-
Monitor the annealing process to prevent thermal shock and ensure that the glass panels are properly annealed before unloading.
Unloading:
-
Once the annealing process is complete and the glass panels have cooled to room temperature, unload them from the furnace.
-
Inspect the tempered glass panels for any defects or imperfections that may have occurred during the tempering process.
-
Package the tempered glass panels for storage or transport, ensuring proper handling to prevent damage.
Maintenance:
-
After completing the tempering process, perform routine maintenance tasks on the furnace to ensure its continued performance and longevity.
-
Clean the furnace components, replace any worn-out parts, and lubricate moving parts as needed.
-
Conduct regular inspections and calibration checks to ensure that the furnace operates efficiently and produces high-quality tempered glass.
By following these steps and maintaining proper control and monitoring throughout the process, glass manufacturers can produce tempered glass panels with consistent quality and performance.